mirror of
https://github.com/superseriousbusiness/gotosocial.git
synced 2025-12-16 16:03:02 -06:00
[chore] bump dependencies (#4339)
- github.com/KimMachineGun/automemlimit v0.7.4 - github.com/miekg/dns v1.1.67 - github.com/minio/minio-go/v7 v7.0.95 - github.com/spf13/pflag v1.0.7 - github.com/tdewolff/minify/v2 v2.23.9 - github.com/uptrace/bun v1.2.15 - github.com/uptrace/bun/dialect/pgdialect v1.2.15 - github.com/uptrace/bun/dialect/sqlitedialect v1.2.15 - github.com/uptrace/bun/extra/bunotel v1.2.15 - golang.org/x/image v0.29.0 - golang.org/x/net v0.42.0 Reviewed-on: https://codeberg.org/superseriousbusiness/gotosocial/pulls/4339 Co-authored-by: kim <grufwub@gmail.com> Co-committed-by: kim <grufwub@gmail.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
eb60081985
commit
c00cad2ceb
76 changed files with 5544 additions and 886 deletions
15
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
15
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
|||
# Binaries for programs and plugins
|
||||
*.exe
|
||||
*.exe~
|
||||
*.dll
|
||||
*.so
|
||||
*.dylib
|
||||
|
||||
# Test binary, built with `go test -c`
|
||||
*.test
|
||||
|
||||
# Output of the go coverage tool, specifically when used with LiteIDE
|
||||
*.out
|
||||
|
||||
# Dependency directories (remove the comment below to include it)
|
||||
# vendor/
|
||||
27
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
27
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
|
||||
met:
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
|
||||
in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
|
||||
distribution.
|
||||
* Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its
|
||||
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
|
||||
this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
"AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
|
||||
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
|
||||
OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
|
||||
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
|
||||
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
|
||||
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
|
||||
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
|
||||
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
12
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
12
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
|||
# Grafana Go regexp package
|
||||
This repo is a fork of the upstream Go `regexp` package, with some code optimisations to make it run faster.
|
||||
|
||||
All the optimisations have been submitted upstream, but not yet merged.
|
||||
|
||||
All semantics are the same, and the optimised code passes all tests from upstream.
|
||||
|
||||
The `main` branch is non-optimised: switch over to [`speedup`](https://github.com/grafana/regexp/tree/speedup) branch for the improved code.
|
||||
|
||||
## Benchmarks:
|
||||
|
||||
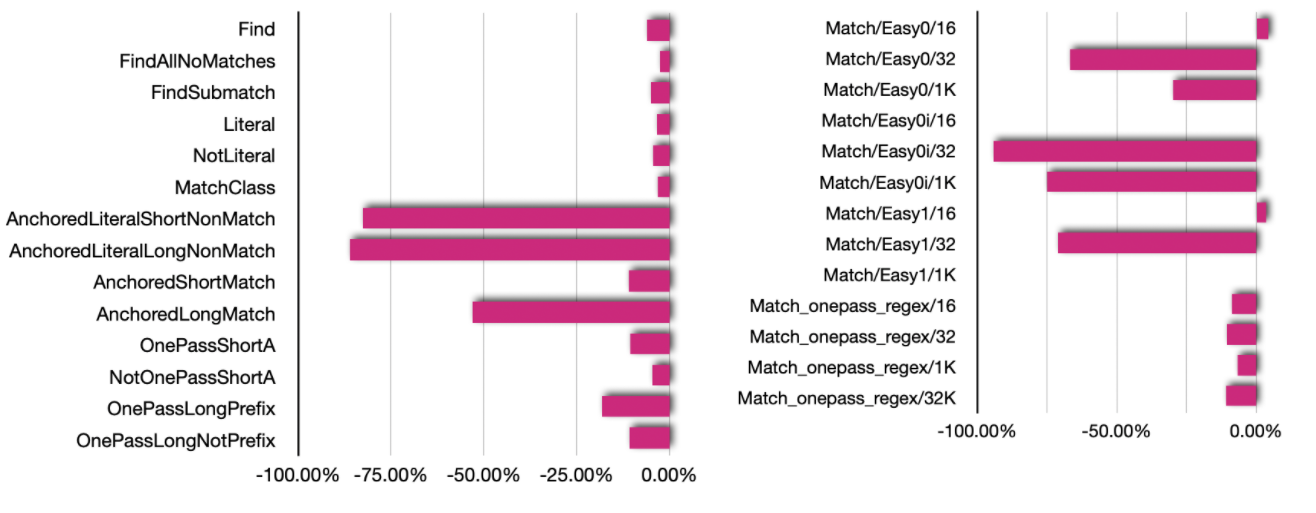
|
||||
365
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/backtrack.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
365
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/backtrack.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,365 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2015 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// backtrack is a regular expression search with submatch
|
||||
// tracking for small regular expressions and texts. It allocates
|
||||
// a bit vector with (length of input) * (length of prog) bits,
|
||||
// to make sure it never explores the same (character position, instruction)
|
||||
// state multiple times. This limits the search to run in time linear in
|
||||
// the length of the test.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// backtrack is a fast replacement for the NFA code on small
|
||||
// regexps when onepass cannot be used.
|
||||
|
||||
package regexp
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"regexp/syntax"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// A job is an entry on the backtracker's job stack. It holds
|
||||
// the instruction pc and the position in the input.
|
||||
type job struct {
|
||||
pc uint32
|
||||
arg bool
|
||||
pos int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
visitedBits = 32
|
||||
maxBacktrackProg = 500 // len(prog.Inst) <= max
|
||||
maxBacktrackVector = 256 * 1024 // bit vector size <= max (bits)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// bitState holds state for the backtracker.
|
||||
type bitState struct {
|
||||
end int
|
||||
cap []int
|
||||
matchcap []int
|
||||
jobs []job
|
||||
visited []uint32
|
||||
|
||||
inputs inputs
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var bitStatePool sync.Pool
|
||||
|
||||
func newBitState() *bitState {
|
||||
b, ok := bitStatePool.Get().(*bitState)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
b = new(bitState)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func freeBitState(b *bitState) {
|
||||
b.inputs.clear()
|
||||
bitStatePool.Put(b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// maxBitStateLen returns the maximum length of a string to search with
|
||||
// the backtracker using prog.
|
||||
func maxBitStateLen(prog *syntax.Prog) int {
|
||||
if !shouldBacktrack(prog) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return maxBacktrackVector / len(prog.Inst)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// shouldBacktrack reports whether the program is too
|
||||
// long for the backtracker to run.
|
||||
func shouldBacktrack(prog *syntax.Prog) bool {
|
||||
return len(prog.Inst) <= maxBacktrackProg
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// reset resets the state of the backtracker.
|
||||
// end is the end position in the input.
|
||||
// ncap is the number of captures.
|
||||
func (b *bitState) reset(prog *syntax.Prog, end int, ncap int) {
|
||||
b.end = end
|
||||
|
||||
if cap(b.jobs) == 0 {
|
||||
b.jobs = make([]job, 0, 256)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.jobs = b.jobs[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
visitedSize := (len(prog.Inst)*(end+1) + visitedBits - 1) / visitedBits
|
||||
if cap(b.visited) < visitedSize {
|
||||
b.visited = make([]uint32, visitedSize, maxBacktrackVector/visitedBits)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.visited = b.visited[:visitedSize]
|
||||
clear(b.visited) // set to 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if cap(b.cap) < ncap {
|
||||
b.cap = make([]int, ncap)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.cap = b.cap[:ncap]
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := range b.cap {
|
||||
b.cap[i] = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if cap(b.matchcap) < ncap {
|
||||
b.matchcap = make([]int, ncap)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.matchcap = b.matchcap[:ncap]
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := range b.matchcap {
|
||||
b.matchcap[i] = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// shouldVisit reports whether the combination of (pc, pos) has not
|
||||
// been visited yet.
|
||||
func (b *bitState) shouldVisit(pc uint32, pos int) bool {
|
||||
n := uint(int(pc)*(b.end+1) + pos)
|
||||
if b.visited[n/visitedBits]&(1<<(n&(visitedBits-1))) != 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.visited[n/visitedBits] |= 1 << (n & (visitedBits - 1))
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// push pushes (pc, pos, arg) onto the job stack if it should be
|
||||
// visited.
|
||||
func (b *bitState) push(re *Regexp, pc uint32, pos int, arg bool) {
|
||||
// Only check shouldVisit when arg is false.
|
||||
// When arg is true, we are continuing a previous visit.
|
||||
if re.prog.Inst[pc].Op != syntax.InstFail && (arg || b.shouldVisit(pc, pos)) {
|
||||
b.jobs = append(b.jobs, job{pc: pc, arg: arg, pos: pos})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// tryBacktrack runs a backtracking search starting at pos.
|
||||
func (re *Regexp) tryBacktrack(b *bitState, i input, pc uint32, pos int) bool {
|
||||
longest := re.longest
|
||||
|
||||
b.push(re, pc, pos, false)
|
||||
for len(b.jobs) > 0 {
|
||||
l := len(b.jobs) - 1
|
||||
// Pop job off the stack.
|
||||
pc := b.jobs[l].pc
|
||||
pos := b.jobs[l].pos
|
||||
arg := b.jobs[l].arg
|
||||
b.jobs = b.jobs[:l]
|
||||
|
||||
// Optimization: rather than push and pop,
|
||||
// code that is going to Push and continue
|
||||
// the loop simply updates ip, p, and arg
|
||||
// and jumps to CheckAndLoop. We have to
|
||||
// do the ShouldVisit check that Push
|
||||
// would have, but we avoid the stack
|
||||
// manipulation.
|
||||
goto Skip
|
||||
CheckAndLoop:
|
||||
if !b.shouldVisit(pc, pos) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
Skip:
|
||||
|
||||
inst := &re.prog.Inst[pc]
|
||||
|
||||
switch inst.Op {
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("bad inst")
|
||||
case syntax.InstFail:
|
||||
panic("unexpected InstFail")
|
||||
case syntax.InstAlt:
|
||||
// Cannot just
|
||||
// b.push(inst.Out, pos, false)
|
||||
// b.push(inst.Arg, pos, false)
|
||||
// If during the processing of inst.Out, we encounter
|
||||
// inst.Arg via another path, we want to process it then.
|
||||
// Pushing it here will inhibit that. Instead, re-push
|
||||
// inst with arg==true as a reminder to push inst.Arg out
|
||||
// later.
|
||||
if arg {
|
||||
// Finished inst.Out; try inst.Arg.
|
||||
arg = false
|
||||
pc = inst.Arg
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.push(re, pc, pos, true)
|
||||
pc = inst.Out
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstAltMatch:
|
||||
// One opcode consumes runes; the other leads to match.
|
||||
switch re.prog.Inst[inst.Out].Op {
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune, syntax.InstRune1, syntax.InstRuneAny, syntax.InstRuneAnyNotNL:
|
||||
// inst.Arg is the match.
|
||||
b.push(re, inst.Arg, pos, false)
|
||||
pc = inst.Arg
|
||||
pos = b.end
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
}
|
||||
// inst.Out is the match - non-greedy
|
||||
b.push(re, inst.Out, b.end, false)
|
||||
pc = inst.Out
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune:
|
||||
r, width := i.step(pos)
|
||||
if !inst.MatchRune(r) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
pos += width
|
||||
pc = inst.Out
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune1:
|
||||
r, width := i.step(pos)
|
||||
if r != inst.Rune[0] {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
pos += width
|
||||
pc = inst.Out
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstRuneAnyNotNL:
|
||||
r, width := i.step(pos)
|
||||
if r == '\n' || r == endOfText {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
pos += width
|
||||
pc = inst.Out
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstRuneAny:
|
||||
r, width := i.step(pos)
|
||||
if r == endOfText {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
pos += width
|
||||
pc = inst.Out
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstCapture:
|
||||
if arg {
|
||||
// Finished inst.Out; restore the old value.
|
||||
b.cap[inst.Arg] = pos
|
||||
continue
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if inst.Arg < uint32(len(b.cap)) {
|
||||
// Capture pos to register, but save old value.
|
||||
b.push(re, pc, b.cap[inst.Arg], true) // come back when we're done.
|
||||
b.cap[inst.Arg] = pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
pc = inst.Out
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstEmptyWidth:
|
||||
flag := i.context(pos)
|
||||
if !flag.match(syntax.EmptyOp(inst.Arg)) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
pc = inst.Out
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstNop:
|
||||
pc = inst.Out
|
||||
goto CheckAndLoop
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstMatch:
|
||||
// We found a match. If the caller doesn't care
|
||||
// where the match is, no point going further.
|
||||
if len(b.cap) == 0 {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Record best match so far.
|
||||
// Only need to check end point, because this entire
|
||||
// call is only considering one start position.
|
||||
if len(b.cap) > 1 {
|
||||
b.cap[1] = pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
if old := b.matchcap[1]; old == -1 || (longest && pos > 0 && pos > old) {
|
||||
copy(b.matchcap, b.cap)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If going for first match, we're done.
|
||||
if !longest {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If we used the entire text, no longer match is possible.
|
||||
if pos == b.end {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, continue on in hope of a longer match.
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return longest && len(b.matchcap) > 1 && b.matchcap[1] >= 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// backtrack runs a backtracking search of prog on the input starting at pos.
|
||||
func (re *Regexp) backtrack(ib []byte, is string, pos int, ncap int, dstCap []int) []int {
|
||||
startCond := re.cond
|
||||
if startCond == ^syntax.EmptyOp(0) { // impossible
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if startCond&syntax.EmptyBeginText != 0 && pos != 0 {
|
||||
// Anchored match, past beginning of text.
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b := newBitState()
|
||||
i, end := b.inputs.init(nil, ib, is)
|
||||
b.reset(re.prog, end, ncap)
|
||||
|
||||
// Anchored search must start at the beginning of the input
|
||||
if startCond&syntax.EmptyBeginText != 0 {
|
||||
if len(b.cap) > 0 {
|
||||
b.cap[0] = pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !re.tryBacktrack(b, i, uint32(re.prog.Start), pos) {
|
||||
freeBitState(b)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
// Unanchored search, starting from each possible text position.
|
||||
// Notice that we have to try the empty string at the end of
|
||||
// the text, so the loop condition is pos <= end, not pos < end.
|
||||
// This looks like it's quadratic in the size of the text,
|
||||
// but we are not clearing visited between calls to TrySearch,
|
||||
// so no work is duplicated and it ends up still being linear.
|
||||
width := -1
|
||||
for ; pos <= end && width != 0; pos += width {
|
||||
if len(re.prefix) > 0 {
|
||||
// Match requires literal prefix; fast search for it.
|
||||
advance := i.index(re, pos)
|
||||
if advance < 0 {
|
||||
freeBitState(b)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
pos += advance
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(b.cap) > 0 {
|
||||
b.cap[0] = pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
if re.tryBacktrack(b, i, uint32(re.prog.Start), pos) {
|
||||
// Match must be leftmost; done.
|
||||
goto Match
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, width = i.step(pos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
freeBitState(b)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Match:
|
||||
dstCap = append(dstCap, b.matchcap...)
|
||||
freeBitState(b)
|
||||
return dstCap
|
||||
}
|
||||
554
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/exec.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
554
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/exec.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,554 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package regexp
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"regexp/syntax"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// A queue is a 'sparse array' holding pending threads of execution.
|
||||
// See https://research.swtch.com/2008/03/using-uninitialized-memory-for-fun-and.html
|
||||
type queue struct {
|
||||
sparse []uint32
|
||||
dense []entry
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// An entry is an entry on a queue.
|
||||
// It holds both the instruction pc and the actual thread.
|
||||
// Some queue entries are just place holders so that the machine
|
||||
// knows it has considered that pc. Such entries have t == nil.
|
||||
type entry struct {
|
||||
pc uint32
|
||||
t *thread
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A thread is the state of a single path through the machine:
|
||||
// an instruction and a corresponding capture array.
|
||||
// See https://swtch.com/~rsc/regexp/regexp2.html
|
||||
type thread struct {
|
||||
inst *syntax.Inst
|
||||
cap []int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A machine holds all the state during an NFA simulation for p.
|
||||
type machine struct {
|
||||
re *Regexp // corresponding Regexp
|
||||
p *syntax.Prog // compiled program
|
||||
q0, q1 queue // two queues for runq, nextq
|
||||
pool []*thread // pool of available threads
|
||||
matched bool // whether a match was found
|
||||
matchcap []int // capture information for the match
|
||||
|
||||
inputs inputs
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type inputs struct {
|
||||
// cached inputs, to avoid allocation
|
||||
bytes inputBytes
|
||||
string inputString
|
||||
reader inputReader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i *inputs) newBytes(b []byte) input {
|
||||
i.bytes.str = b
|
||||
return &i.bytes
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i *inputs) newString(s string) input {
|
||||
i.string.str = s
|
||||
return &i.string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i *inputs) newReader(r io.RuneReader) input {
|
||||
i.reader.r = r
|
||||
i.reader.atEOT = false
|
||||
i.reader.pos = 0
|
||||
return &i.reader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i *inputs) clear() {
|
||||
// We need to clear 1 of these.
|
||||
// Avoid the expense of clearing the others (pointer write barrier).
|
||||
if i.bytes.str != nil {
|
||||
i.bytes.str = nil
|
||||
} else if i.reader.r != nil {
|
||||
i.reader.r = nil
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
i.string.str = ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i *inputs) init(r io.RuneReader, b []byte, s string) (input, int) {
|
||||
if r != nil {
|
||||
return i.newReader(r), 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if b != nil {
|
||||
return i.newBytes(b), len(b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i.newString(s), len(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *machine) init(ncap int) {
|
||||
for _, t := range m.pool {
|
||||
t.cap = t.cap[:ncap]
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.matchcap = m.matchcap[:ncap]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// alloc allocates a new thread with the given instruction.
|
||||
// It uses the free pool if possible.
|
||||
func (m *machine) alloc(i *syntax.Inst) *thread {
|
||||
var t *thread
|
||||
if n := len(m.pool); n > 0 {
|
||||
t = m.pool[n-1]
|
||||
m.pool = m.pool[:n-1]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
t = new(thread)
|
||||
t.cap = make([]int, len(m.matchcap), cap(m.matchcap))
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.inst = i
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A lazyFlag is a lazily-evaluated syntax.EmptyOp,
|
||||
// for checking zero-width flags like ^ $ \A \z \B \b.
|
||||
// It records the pair of relevant runes and does not
|
||||
// determine the implied flags until absolutely necessary
|
||||
// (most of the time, that means never).
|
||||
type lazyFlag uint64
|
||||
|
||||
func newLazyFlag(r1, r2 rune) lazyFlag {
|
||||
return lazyFlag(uint64(r1)<<32 | uint64(uint32(r2)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f lazyFlag) match(op syntax.EmptyOp) bool {
|
||||
if op == 0 {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
r1 := rune(f >> 32)
|
||||
if op&syntax.EmptyBeginLine != 0 {
|
||||
if r1 != '\n' && r1 >= 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
op &^= syntax.EmptyBeginLine
|
||||
}
|
||||
if op&syntax.EmptyBeginText != 0 {
|
||||
if r1 >= 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
op &^= syntax.EmptyBeginText
|
||||
}
|
||||
if op == 0 {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
r2 := rune(f)
|
||||
if op&syntax.EmptyEndLine != 0 {
|
||||
if r2 != '\n' && r2 >= 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
op &^= syntax.EmptyEndLine
|
||||
}
|
||||
if op&syntax.EmptyEndText != 0 {
|
||||
if r2 >= 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
op &^= syntax.EmptyEndText
|
||||
}
|
||||
if op == 0 {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
if syntax.IsWordChar(r1) != syntax.IsWordChar(r2) {
|
||||
op &^= syntax.EmptyWordBoundary
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
op &^= syntax.EmptyNoWordBoundary
|
||||
}
|
||||
return op == 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// match runs the machine over the input starting at pos.
|
||||
// It reports whether a match was found.
|
||||
// If so, m.matchcap holds the submatch information.
|
||||
func (m *machine) match(i input, pos int) bool {
|
||||
startCond := m.re.cond
|
||||
if startCond == ^syntax.EmptyOp(0) { // impossible
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.matched = false
|
||||
for i := range m.matchcap {
|
||||
m.matchcap[i] = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
runq, nextq := &m.q0, &m.q1
|
||||
r, r1 := endOfText, endOfText
|
||||
width, width1 := 0, 0
|
||||
r, width = i.step(pos)
|
||||
if r != endOfText {
|
||||
r1, width1 = i.step(pos + width)
|
||||
}
|
||||
var flag lazyFlag
|
||||
if pos == 0 {
|
||||
flag = newLazyFlag(-1, r)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
flag = i.context(pos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if len(runq.dense) == 0 {
|
||||
if startCond&syntax.EmptyBeginText != 0 && pos != 0 {
|
||||
// Anchored match, past beginning of text.
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if m.matched {
|
||||
// Have match; finished exploring alternatives.
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(m.re.prefix) > 0 && r1 != m.re.prefixRune && i.canCheckPrefix() {
|
||||
// Match requires literal prefix; fast search for it.
|
||||
advance := i.index(m.re, pos)
|
||||
if advance < 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
pos += advance
|
||||
r, width = i.step(pos)
|
||||
r1, width1 = i.step(pos + width)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !m.matched {
|
||||
if len(m.matchcap) > 0 {
|
||||
m.matchcap[0] = pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.add(runq, uint32(m.p.Start), pos, m.matchcap, &flag, nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
flag = newLazyFlag(r, r1)
|
||||
m.step(runq, nextq, pos, pos+width, r, &flag)
|
||||
if width == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(m.matchcap) == 0 && m.matched {
|
||||
// Found a match and not paying attention
|
||||
// to where it is, so any match will do.
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
pos += width
|
||||
r, width = r1, width1
|
||||
if r != endOfText {
|
||||
r1, width1 = i.step(pos + width)
|
||||
}
|
||||
runq, nextq = nextq, runq
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.clear(nextq)
|
||||
return m.matched
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clear frees all threads on the thread queue.
|
||||
func (m *machine) clear(q *queue) {
|
||||
for _, d := range q.dense {
|
||||
if d.t != nil {
|
||||
m.pool = append(m.pool, d.t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
q.dense = q.dense[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// step executes one step of the machine, running each of the threads
|
||||
// on runq and appending new threads to nextq.
|
||||
// The step processes the rune c (which may be endOfText),
|
||||
// which starts at position pos and ends at nextPos.
|
||||
// nextCond gives the setting for the empty-width flags after c.
|
||||
func (m *machine) step(runq, nextq *queue, pos, nextPos int, c rune, nextCond *lazyFlag) {
|
||||
longest := m.re.longest
|
||||
for j := 0; j < len(runq.dense); j++ {
|
||||
d := &runq.dense[j]
|
||||
t := d.t
|
||||
if t == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if longest && m.matched && len(t.cap) > 0 && m.matchcap[0] < t.cap[0] {
|
||||
m.pool = append(m.pool, t)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
i := t.inst
|
||||
add := false
|
||||
switch i.Op {
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("bad inst")
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstMatch:
|
||||
if len(t.cap) > 0 && (!longest || !m.matched || m.matchcap[1] < pos) {
|
||||
t.cap[1] = pos
|
||||
copy(m.matchcap, t.cap)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !longest {
|
||||
// First-match mode: cut off all lower-priority threads.
|
||||
for _, d := range runq.dense[j+1:] {
|
||||
if d.t != nil {
|
||||
m.pool = append(m.pool, d.t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
runq.dense = runq.dense[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.matched = true
|
||||
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune:
|
||||
add = i.MatchRune(c)
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune1:
|
||||
add = c == i.Rune[0]
|
||||
case syntax.InstRuneAny:
|
||||
add = true
|
||||
case syntax.InstRuneAnyNotNL:
|
||||
add = c != '\n'
|
||||
}
|
||||
if add {
|
||||
t = m.add(nextq, i.Out, nextPos, t.cap, nextCond, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t != nil {
|
||||
m.pool = append(m.pool, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
runq.dense = runq.dense[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// add adds an entry to q for pc, unless the q already has such an entry.
|
||||
// It also recursively adds an entry for all instructions reachable from pc by following
|
||||
// empty-width conditions satisfied by cond. pos gives the current position
|
||||
// in the input.
|
||||
func (m *machine) add(q *queue, pc uint32, pos int, cap []int, cond *lazyFlag, t *thread) *thread {
|
||||
Again:
|
||||
if pc == 0 {
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
if j := q.sparse[pc]; j < uint32(len(q.dense)) && q.dense[j].pc == pc {
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
j := len(q.dense)
|
||||
q.dense = q.dense[:j+1]
|
||||
d := &q.dense[j]
|
||||
d.t = nil
|
||||
d.pc = pc
|
||||
q.sparse[pc] = uint32(j)
|
||||
|
||||
i := &m.p.Inst[pc]
|
||||
switch i.Op {
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("unhandled")
|
||||
case syntax.InstFail:
|
||||
// nothing
|
||||
case syntax.InstAlt, syntax.InstAltMatch:
|
||||
t = m.add(q, i.Out, pos, cap, cond, t)
|
||||
pc = i.Arg
|
||||
goto Again
|
||||
case syntax.InstEmptyWidth:
|
||||
if cond.match(syntax.EmptyOp(i.Arg)) {
|
||||
pc = i.Out
|
||||
goto Again
|
||||
}
|
||||
case syntax.InstNop:
|
||||
pc = i.Out
|
||||
goto Again
|
||||
case syntax.InstCapture:
|
||||
if int(i.Arg) < len(cap) {
|
||||
opos := cap[i.Arg]
|
||||
cap[i.Arg] = pos
|
||||
m.add(q, i.Out, pos, cap, cond, nil)
|
||||
cap[i.Arg] = opos
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
pc = i.Out
|
||||
goto Again
|
||||
}
|
||||
case syntax.InstMatch, syntax.InstRune, syntax.InstRune1, syntax.InstRuneAny, syntax.InstRuneAnyNotNL:
|
||||
if t == nil {
|
||||
t = m.alloc(i)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
t.inst = i
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(cap) > 0 && &t.cap[0] != &cap[0] {
|
||||
copy(t.cap, cap)
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.t = t
|
||||
t = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type onePassMachine struct {
|
||||
inputs inputs
|
||||
matchcap []int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var onePassPool sync.Pool
|
||||
|
||||
func newOnePassMachine() *onePassMachine {
|
||||
m, ok := onePassPool.Get().(*onePassMachine)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
m = new(onePassMachine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func freeOnePassMachine(m *onePassMachine) {
|
||||
m.inputs.clear()
|
||||
onePassPool.Put(m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// doOnePass implements r.doExecute using the one-pass execution engine.
|
||||
func (re *Regexp) doOnePass(ir io.RuneReader, ib []byte, is string, pos, ncap int, dstCap []int) []int {
|
||||
startCond := re.cond
|
||||
if startCond == ^syntax.EmptyOp(0) { // impossible
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
m := newOnePassMachine()
|
||||
if cap(m.matchcap) < ncap {
|
||||
m.matchcap = make([]int, ncap)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
m.matchcap = m.matchcap[:ncap]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
matched := false
|
||||
for i := range m.matchcap {
|
||||
m.matchcap[i] = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
i, _ := m.inputs.init(ir, ib, is)
|
||||
|
||||
r, r1 := endOfText, endOfText
|
||||
width, width1 := 0, 0
|
||||
r, width = i.step(pos)
|
||||
if r != endOfText {
|
||||
r1, width1 = i.step(pos + width)
|
||||
}
|
||||
var flag lazyFlag
|
||||
if pos == 0 {
|
||||
flag = newLazyFlag(-1, r)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
flag = i.context(pos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
pc := re.onepass.Start
|
||||
inst := &re.onepass.Inst[pc]
|
||||
// If there is a simple literal prefix, skip over it.
|
||||
if pos == 0 && flag.match(syntax.EmptyOp(inst.Arg)) &&
|
||||
len(re.prefix) > 0 && i.canCheckPrefix() {
|
||||
// Match requires literal prefix; fast search for it.
|
||||
if !i.hasPrefix(re) {
|
||||
goto Return
|
||||
}
|
||||
pos += len(re.prefix)
|
||||
r, width = i.step(pos)
|
||||
r1, width1 = i.step(pos + width)
|
||||
flag = i.context(pos)
|
||||
pc = int(re.prefixEnd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for {
|
||||
inst = &re.onepass.Inst[pc]
|
||||
pc = int(inst.Out)
|
||||
switch inst.Op {
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("bad inst")
|
||||
case syntax.InstMatch:
|
||||
matched = true
|
||||
if len(m.matchcap) > 0 {
|
||||
m.matchcap[0] = 0
|
||||
m.matchcap[1] = pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
goto Return
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune:
|
||||
if !inst.MatchRune(r) {
|
||||
goto Return
|
||||
}
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune1:
|
||||
if r != inst.Rune[0] {
|
||||
goto Return
|
||||
}
|
||||
case syntax.InstRuneAny:
|
||||
// Nothing
|
||||
case syntax.InstRuneAnyNotNL:
|
||||
if r == '\n' {
|
||||
goto Return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// peek at the input rune to see which branch of the Alt to take
|
||||
case syntax.InstAlt, syntax.InstAltMatch:
|
||||
pc = int(onePassNext(inst, r))
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case syntax.InstFail:
|
||||
goto Return
|
||||
case syntax.InstNop:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case syntax.InstEmptyWidth:
|
||||
if !flag.match(syntax.EmptyOp(inst.Arg)) {
|
||||
goto Return
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case syntax.InstCapture:
|
||||
if int(inst.Arg) < len(m.matchcap) {
|
||||
m.matchcap[inst.Arg] = pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if width == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
flag = newLazyFlag(r, r1)
|
||||
pos += width
|
||||
r, width = r1, width1
|
||||
if r != endOfText {
|
||||
r1, width1 = i.step(pos + width)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Return:
|
||||
if !matched {
|
||||
freeOnePassMachine(m)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dstCap = append(dstCap, m.matchcap...)
|
||||
freeOnePassMachine(m)
|
||||
return dstCap
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// doMatch reports whether either r, b or s match the regexp.
|
||||
func (re *Regexp) doMatch(r io.RuneReader, b []byte, s string) bool {
|
||||
return re.doExecute(r, b, s, 0, 0, nil) != nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// doExecute finds the leftmost match in the input, appends the position
|
||||
// of its subexpressions to dstCap and returns dstCap.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// nil is returned if no matches are found and non-nil if matches are found.
|
||||
func (re *Regexp) doExecute(r io.RuneReader, b []byte, s string, pos int, ncap int, dstCap []int) []int {
|
||||
if dstCap == nil {
|
||||
// Make sure 'return dstCap' is non-nil.
|
||||
dstCap = arrayNoInts[:0:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if r == nil && len(b)+len(s) < re.minInputLen {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if re.onepass != nil {
|
||||
return re.doOnePass(r, b, s, pos, ncap, dstCap)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if r == nil && len(b)+len(s) < re.maxBitStateLen {
|
||||
return re.backtrack(b, s, pos, ncap, dstCap)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
m := re.get()
|
||||
i, _ := m.inputs.init(r, b, s)
|
||||
|
||||
m.init(ncap)
|
||||
if !m.match(i, pos) {
|
||||
re.put(m)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dstCap = append(dstCap, m.matchcap...)
|
||||
re.put(m)
|
||||
return dstCap
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// arrayNoInts is returned by doExecute match if nil dstCap is passed
|
||||
// to it with ncap=0.
|
||||
var arrayNoInts [0]int
|
||||
500
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/onepass.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
500
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/onepass.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,500 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package regexp
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"regexp/syntax"
|
||||
"slices"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// "One-pass" regexp execution.
|
||||
// Some regexps can be analyzed to determine that they never need
|
||||
// backtracking: they are guaranteed to run in one pass over the string
|
||||
// without bothering to save all the usual NFA state.
|
||||
// Detect those and execute them more quickly.
|
||||
|
||||
// A onePassProg is a compiled one-pass regular expression program.
|
||||
// It is the same as syntax.Prog except for the use of onePassInst.
|
||||
type onePassProg struct {
|
||||
Inst []onePassInst
|
||||
Start int // index of start instruction
|
||||
NumCap int // number of InstCapture insts in re
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A onePassInst is a single instruction in a one-pass regular expression program.
|
||||
// It is the same as syntax.Inst except for the new 'Next' field.
|
||||
type onePassInst struct {
|
||||
syntax.Inst
|
||||
Next []uint32
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// onePassPrefix returns a literal string that all matches for the
|
||||
// regexp must start with. Complete is true if the prefix
|
||||
// is the entire match. Pc is the index of the last rune instruction
|
||||
// in the string. The onePassPrefix skips over the mandatory
|
||||
// EmptyBeginText.
|
||||
func onePassPrefix(p *syntax.Prog) (prefix string, complete bool, pc uint32) {
|
||||
i := &p.Inst[p.Start]
|
||||
if i.Op != syntax.InstEmptyWidth || (syntax.EmptyOp(i.Arg))&syntax.EmptyBeginText == 0 {
|
||||
return "", i.Op == syntax.InstMatch, uint32(p.Start)
|
||||
}
|
||||
pc = i.Out
|
||||
i = &p.Inst[pc]
|
||||
for i.Op == syntax.InstNop {
|
||||
pc = i.Out
|
||||
i = &p.Inst[pc]
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Avoid allocation of buffer if prefix is empty.
|
||||
if iop(i) != syntax.InstRune || len(i.Rune) != 1 {
|
||||
return "", i.Op == syntax.InstMatch, uint32(p.Start)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Have prefix; gather characters.
|
||||
var buf strings.Builder
|
||||
for iop(i) == syntax.InstRune && len(i.Rune) == 1 && syntax.Flags(i.Arg)&syntax.FoldCase == 0 && i.Rune[0] != utf8.RuneError {
|
||||
buf.WriteRune(i.Rune[0])
|
||||
pc, i = i.Out, &p.Inst[i.Out]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.Op == syntax.InstEmptyWidth &&
|
||||
syntax.EmptyOp(i.Arg)&syntax.EmptyEndText != 0 &&
|
||||
p.Inst[i.Out].Op == syntax.InstMatch {
|
||||
complete = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return buf.String(), complete, pc
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// onePassNext selects the next actionable state of the prog, based on the input character.
|
||||
// It should only be called when i.Op == InstAlt or InstAltMatch, and from the one-pass machine.
|
||||
// One of the alternates may ultimately lead without input to end of line. If the instruction
|
||||
// is InstAltMatch the path to the InstMatch is in i.Out, the normal node in i.Next.
|
||||
func onePassNext(i *onePassInst, r rune) uint32 {
|
||||
next := i.MatchRunePos(r)
|
||||
if next >= 0 {
|
||||
return i.Next[next]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.Op == syntax.InstAltMatch {
|
||||
return i.Out
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func iop(i *syntax.Inst) syntax.InstOp {
|
||||
op := i.Op
|
||||
switch op {
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune1, syntax.InstRuneAny, syntax.InstRuneAnyNotNL:
|
||||
op = syntax.InstRune
|
||||
}
|
||||
return op
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sparse Array implementation is used as a queueOnePass.
|
||||
type queueOnePass struct {
|
||||
sparse []uint32
|
||||
dense []uint32
|
||||
size, nextIndex uint32
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (q *queueOnePass) empty() bool {
|
||||
return q.nextIndex >= q.size
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (q *queueOnePass) next() (n uint32) {
|
||||
n = q.dense[q.nextIndex]
|
||||
q.nextIndex++
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (q *queueOnePass) clear() {
|
||||
q.size = 0
|
||||
q.nextIndex = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (q *queueOnePass) contains(u uint32) bool {
|
||||
if u >= uint32(len(q.sparse)) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return q.sparse[u] < q.size && q.dense[q.sparse[u]] == u
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (q *queueOnePass) insert(u uint32) {
|
||||
if !q.contains(u) {
|
||||
q.insertNew(u)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (q *queueOnePass) insertNew(u uint32) {
|
||||
if u >= uint32(len(q.sparse)) {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
q.sparse[u] = q.size
|
||||
q.dense[q.size] = u
|
||||
q.size++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func newQueue(size int) (q *queueOnePass) {
|
||||
return &queueOnePass{
|
||||
sparse: make([]uint32, size),
|
||||
dense: make([]uint32, size),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// mergeRuneSets merges two non-intersecting runesets, and returns the merged result,
|
||||
// and a NextIp array. The idea is that if a rune matches the OnePassRunes at index
|
||||
// i, NextIp[i/2] is the target. If the input sets intersect, an empty runeset and a
|
||||
// NextIp array with the single element mergeFailed is returned.
|
||||
// The code assumes that both inputs contain ordered and non-intersecting rune pairs.
|
||||
const mergeFailed = uint32(0xffffffff)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
noRune = []rune{}
|
||||
noNext = []uint32{mergeFailed}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func mergeRuneSets(leftRunes, rightRunes *[]rune, leftPC, rightPC uint32) ([]rune, []uint32) {
|
||||
leftLen := len(*leftRunes)
|
||||
rightLen := len(*rightRunes)
|
||||
if leftLen&0x1 != 0 || rightLen&0x1 != 0 {
|
||||
panic("mergeRuneSets odd length []rune")
|
||||
}
|
||||
var (
|
||||
lx, rx int
|
||||
)
|
||||
merged := make([]rune, 0)
|
||||
next := make([]uint32, 0)
|
||||
ok := true
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
merged = nil
|
||||
next = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
ix := -1
|
||||
extend := func(newLow *int, newArray *[]rune, pc uint32) bool {
|
||||
if ix > 0 && (*newArray)[*newLow] <= merged[ix] {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
merged = append(merged, (*newArray)[*newLow], (*newArray)[*newLow+1])
|
||||
*newLow += 2
|
||||
ix += 2
|
||||
next = append(next, pc)
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for lx < leftLen || rx < rightLen {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case rx >= rightLen:
|
||||
ok = extend(&lx, leftRunes, leftPC)
|
||||
case lx >= leftLen:
|
||||
ok = extend(&rx, rightRunes, rightPC)
|
||||
case (*rightRunes)[rx] < (*leftRunes)[lx]:
|
||||
ok = extend(&rx, rightRunes, rightPC)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
ok = extend(&lx, leftRunes, leftPC)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return noRune, noNext
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return merged, next
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// cleanupOnePass drops working memory, and restores certain shortcut instructions.
|
||||
func cleanupOnePass(prog *onePassProg, original *syntax.Prog) {
|
||||
for ix, instOriginal := range original.Inst {
|
||||
switch instOriginal.Op {
|
||||
case syntax.InstAlt, syntax.InstAltMatch, syntax.InstRune:
|
||||
case syntax.InstCapture, syntax.InstEmptyWidth, syntax.InstNop, syntax.InstMatch, syntax.InstFail:
|
||||
prog.Inst[ix].Next = nil
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune1, syntax.InstRuneAny, syntax.InstRuneAnyNotNL:
|
||||
prog.Inst[ix].Next = nil
|
||||
prog.Inst[ix] = onePassInst{Inst: instOriginal}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// onePassCopy creates a copy of the original Prog, as we'll be modifying it.
|
||||
func onePassCopy(prog *syntax.Prog) *onePassProg {
|
||||
p := &onePassProg{
|
||||
Start: prog.Start,
|
||||
NumCap: prog.NumCap,
|
||||
Inst: make([]onePassInst, len(prog.Inst)),
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i, inst := range prog.Inst {
|
||||
p.Inst[i] = onePassInst{Inst: inst}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// rewrites one or more common Prog constructs that enable some otherwise
|
||||
// non-onepass Progs to be onepass. A:BD (for example) means an InstAlt at
|
||||
// ip A, that points to ips B & C.
|
||||
// A:BC + B:DA => A:BC + B:CD
|
||||
// A:BC + B:DC => A:DC + B:DC
|
||||
for pc := range p.Inst {
|
||||
switch p.Inst[pc].Op {
|
||||
default:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case syntax.InstAlt, syntax.InstAltMatch:
|
||||
// A:Bx + B:Ay
|
||||
p_A_Other := &p.Inst[pc].Out
|
||||
p_A_Alt := &p.Inst[pc].Arg
|
||||
// make sure a target is another Alt
|
||||
instAlt := p.Inst[*p_A_Alt]
|
||||
if !(instAlt.Op == syntax.InstAlt || instAlt.Op == syntax.InstAltMatch) {
|
||||
p_A_Alt, p_A_Other = p_A_Other, p_A_Alt
|
||||
instAlt = p.Inst[*p_A_Alt]
|
||||
if !(instAlt.Op == syntax.InstAlt || instAlt.Op == syntax.InstAltMatch) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
instOther := p.Inst[*p_A_Other]
|
||||
// Analyzing both legs pointing to Alts is for another day
|
||||
if instOther.Op == syntax.InstAlt || instOther.Op == syntax.InstAltMatch {
|
||||
// too complicated
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
// simple empty transition loop
|
||||
// A:BC + B:DA => A:BC + B:DC
|
||||
p_B_Alt := &p.Inst[*p_A_Alt].Out
|
||||
p_B_Other := &p.Inst[*p_A_Alt].Arg
|
||||
patch := false
|
||||
if instAlt.Out == uint32(pc) {
|
||||
patch = true
|
||||
} else if instAlt.Arg == uint32(pc) {
|
||||
patch = true
|
||||
p_B_Alt, p_B_Other = p_B_Other, p_B_Alt
|
||||
}
|
||||
if patch {
|
||||
*p_B_Alt = *p_A_Other
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// empty transition to common target
|
||||
// A:BC + B:DC => A:DC + B:DC
|
||||
if *p_A_Other == *p_B_Alt {
|
||||
*p_A_Alt = *p_B_Other
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var anyRuneNotNL = []rune{0, '\n' - 1, '\n' + 1, unicode.MaxRune}
|
||||
var anyRune = []rune{0, unicode.MaxRune}
|
||||
|
||||
// makeOnePass creates a onepass Prog, if possible. It is possible if at any alt,
|
||||
// the match engine can always tell which branch to take. The routine may modify
|
||||
// p if it is turned into a onepass Prog. If it isn't possible for this to be a
|
||||
// onepass Prog, the Prog nil is returned. makeOnePass is recursive
|
||||
// to the size of the Prog.
|
||||
func makeOnePass(p *onePassProg) *onePassProg {
|
||||
// If the machine is very long, it's not worth the time to check if we can use one pass.
|
||||
if len(p.Inst) >= 1000 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
instQueue = newQueue(len(p.Inst))
|
||||
visitQueue = newQueue(len(p.Inst))
|
||||
check func(uint32, []bool) bool
|
||||
onePassRunes = make([][]rune, len(p.Inst))
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// check that paths from Alt instructions are unambiguous, and rebuild the new
|
||||
// program as a onepass program
|
||||
check = func(pc uint32, m []bool) (ok bool) {
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
inst := &p.Inst[pc]
|
||||
if visitQueue.contains(pc) {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
visitQueue.insert(pc)
|
||||
switch inst.Op {
|
||||
case syntax.InstAlt, syntax.InstAltMatch:
|
||||
ok = check(inst.Out, m) && check(inst.Arg, m)
|
||||
// check no-input paths to InstMatch
|
||||
matchOut := m[inst.Out]
|
||||
matchArg := m[inst.Arg]
|
||||
if matchOut && matchArg {
|
||||
ok = false
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Match on empty goes in inst.Out
|
||||
if matchArg {
|
||||
inst.Out, inst.Arg = inst.Arg, inst.Out
|
||||
matchOut, matchArg = matchArg, matchOut
|
||||
}
|
||||
if matchOut {
|
||||
m[pc] = true
|
||||
inst.Op = syntax.InstAltMatch
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// build a dispatch operator from the two legs of the alt.
|
||||
onePassRunes[pc], inst.Next = mergeRuneSets(
|
||||
&onePassRunes[inst.Out], &onePassRunes[inst.Arg], inst.Out, inst.Arg)
|
||||
if len(inst.Next) > 0 && inst.Next[0] == mergeFailed {
|
||||
ok = false
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
case syntax.InstCapture, syntax.InstNop:
|
||||
ok = check(inst.Out, m)
|
||||
m[pc] = m[inst.Out]
|
||||
// pass matching runes back through these no-ops.
|
||||
onePassRunes[pc] = append([]rune{}, onePassRunes[inst.Out]...)
|
||||
inst.Next = make([]uint32, len(onePassRunes[pc])/2+1)
|
||||
for i := range inst.Next {
|
||||
inst.Next[i] = inst.Out
|
||||
}
|
||||
case syntax.InstEmptyWidth:
|
||||
ok = check(inst.Out, m)
|
||||
m[pc] = m[inst.Out]
|
||||
onePassRunes[pc] = append([]rune{}, onePassRunes[inst.Out]...)
|
||||
inst.Next = make([]uint32, len(onePassRunes[pc])/2+1)
|
||||
for i := range inst.Next {
|
||||
inst.Next[i] = inst.Out
|
||||
}
|
||||
case syntax.InstMatch, syntax.InstFail:
|
||||
m[pc] = inst.Op == syntax.InstMatch
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune:
|
||||
m[pc] = false
|
||||
if len(inst.Next) > 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
instQueue.insert(inst.Out)
|
||||
if len(inst.Rune) == 0 {
|
||||
onePassRunes[pc] = []rune{}
|
||||
inst.Next = []uint32{inst.Out}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
runes := make([]rune, 0)
|
||||
if len(inst.Rune) == 1 && syntax.Flags(inst.Arg)&syntax.FoldCase != 0 {
|
||||
r0 := inst.Rune[0]
|
||||
runes = append(runes, r0, r0)
|
||||
for r1 := unicode.SimpleFold(r0); r1 != r0; r1 = unicode.SimpleFold(r1) {
|
||||
runes = append(runes, r1, r1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
slices.Sort(runes)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
runes = append(runes, inst.Rune...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
onePassRunes[pc] = runes
|
||||
inst.Next = make([]uint32, len(onePassRunes[pc])/2+1)
|
||||
for i := range inst.Next {
|
||||
inst.Next[i] = inst.Out
|
||||
}
|
||||
inst.Op = syntax.InstRune
|
||||
case syntax.InstRune1:
|
||||
m[pc] = false
|
||||
if len(inst.Next) > 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
instQueue.insert(inst.Out)
|
||||
runes := []rune{}
|
||||
// expand case-folded runes
|
||||
if syntax.Flags(inst.Arg)&syntax.FoldCase != 0 {
|
||||
r0 := inst.Rune[0]
|
||||
runes = append(runes, r0, r0)
|
||||
for r1 := unicode.SimpleFold(r0); r1 != r0; r1 = unicode.SimpleFold(r1) {
|
||||
runes = append(runes, r1, r1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
slices.Sort(runes)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
runes = append(runes, inst.Rune[0], inst.Rune[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
onePassRunes[pc] = runes
|
||||
inst.Next = make([]uint32, len(onePassRunes[pc])/2+1)
|
||||
for i := range inst.Next {
|
||||
inst.Next[i] = inst.Out
|
||||
}
|
||||
inst.Op = syntax.InstRune
|
||||
case syntax.InstRuneAny:
|
||||
m[pc] = false
|
||||
if len(inst.Next) > 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
instQueue.insert(inst.Out)
|
||||
onePassRunes[pc] = append([]rune{}, anyRune...)
|
||||
inst.Next = []uint32{inst.Out}
|
||||
case syntax.InstRuneAnyNotNL:
|
||||
m[pc] = false
|
||||
if len(inst.Next) > 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
instQueue.insert(inst.Out)
|
||||
onePassRunes[pc] = append([]rune{}, anyRuneNotNL...)
|
||||
inst.Next = make([]uint32, len(onePassRunes[pc])/2+1)
|
||||
for i := range inst.Next {
|
||||
inst.Next[i] = inst.Out
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
instQueue.clear()
|
||||
instQueue.insert(uint32(p.Start))
|
||||
m := make([]bool, len(p.Inst))
|
||||
for !instQueue.empty() {
|
||||
visitQueue.clear()
|
||||
pc := instQueue.next()
|
||||
if !check(pc, m) {
|
||||
p = nil
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
for i := range p.Inst {
|
||||
p.Inst[i].Rune = onePassRunes[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// compileOnePass returns a new *syntax.Prog suitable for onePass execution if the original Prog
|
||||
// can be recharacterized as a one-pass regexp program, or syntax.nil if the
|
||||
// Prog cannot be converted. For a one pass prog, the fundamental condition that must
|
||||
// be true is: at any InstAlt, there must be no ambiguity about what branch to take.
|
||||
func compileOnePass(prog *syntax.Prog) (p *onePassProg) {
|
||||
if prog.Start == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// onepass regexp is anchored
|
||||
if prog.Inst[prog.Start].Op != syntax.InstEmptyWidth ||
|
||||
syntax.EmptyOp(prog.Inst[prog.Start].Arg)&syntax.EmptyBeginText != syntax.EmptyBeginText {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// every instruction leading to InstMatch must be EmptyEndText
|
||||
for _, inst := range prog.Inst {
|
||||
opOut := prog.Inst[inst.Out].Op
|
||||
switch inst.Op {
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if opOut == syntax.InstMatch {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
case syntax.InstAlt, syntax.InstAltMatch:
|
||||
if opOut == syntax.InstMatch || prog.Inst[inst.Arg].Op == syntax.InstMatch {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
case syntax.InstEmptyWidth:
|
||||
if opOut == syntax.InstMatch {
|
||||
if syntax.EmptyOp(inst.Arg)&syntax.EmptyEndText == syntax.EmptyEndText {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Creates a slightly optimized copy of the original Prog
|
||||
// that cleans up some Prog idioms that block valid onepass programs
|
||||
p = onePassCopy(prog)
|
||||
|
||||
// checkAmbiguity on InstAlts, build onepass Prog if possible
|
||||
p = makeOnePass(p)
|
||||
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
cleanupOnePass(p, prog)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
1304
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/regexp.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
1304
vendor/github.com/grafana/regexp/regexp.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue